CHAPTER - 8
IPO (Initial Public Offer)
Every business person or an entrepreneur starts up with a business idea & limited capital. The business evolves with time. During this period, the company is financially supported by loans, venture capital & private equity.
A venture capitalist is an investor who invests in the business at an early stage.
Then comes the stage where the company has progressed well. The revenues & profits are good & the investors are happy with the returns on investment. But, the promoters aim to expand the business further; let's say the company wants to go international. This will require heavy investments in real estate, research, manufacturing capacities, investment in people, etc.
The company has many options like internal accruals, bank loans, issue bonds, an IPO, or a combination.

But filing an IPO can prove to be a good option as compared to other options as the public offer has its advantages:
1. The company can raise funds without adding up to the liabilities of the company.
2. In a public offer, the promoters can sell off their stake in the company & exit from the company.
3. ESOP: The company employees get shares of the company as an incentive for good performance in the company. Listing of the company can benefit employees as they would enjoy the capital appreciation in its shares.
4. Accelerate company growth: When the company gets listed on the stock exchange, people talk about the company, research about the company & invest in the company. As a result, it boosts the growth of the company.
An Initial Public Offer is a primary market of the shares. Once the shares get listed on the exchange, the shares are traded publicly. This is called a secondary market.
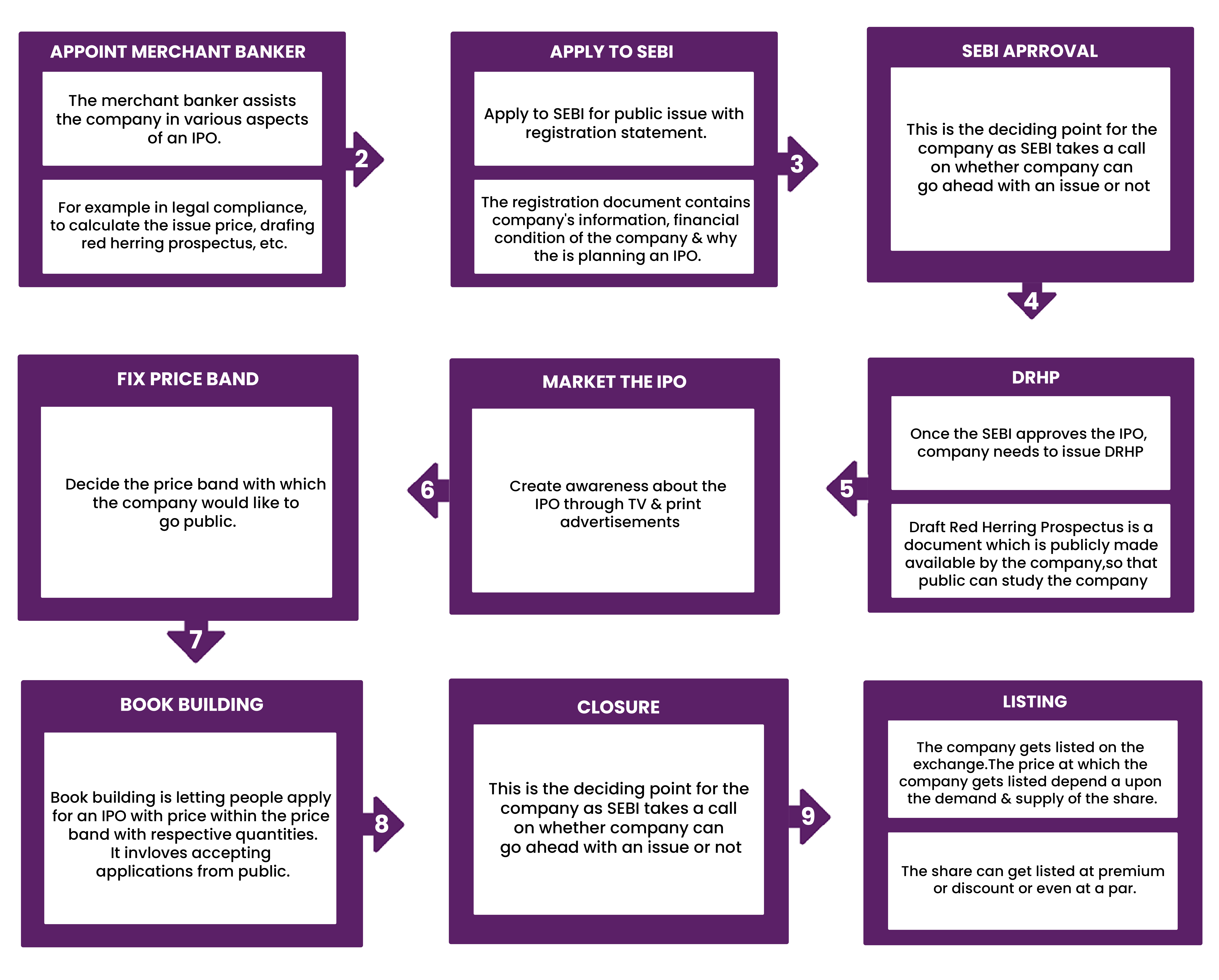
The process of an IPO in a nutshell:
SEBI regulates the process of an IPO.